Multiple Linear Regression
Click here to open the slides.
Here is the R script for analyzing the tutorial dataset:
library(openintro)
library(ggplot2)
data("tourism", package = 'openintro') # Question 8.21
ggplot(tourism, aes(x = visitor_count_tho)) +
geom_histogram()
ggplot(tourism, aes(x = tourist_spending)) +
geom_histogram()
ggplot(tourism, aes(x = visitor_count_tho, y = tourist_spending)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = 'lm', se = FALSE, formula = y ~ x) +
scale_x_log10() + scale_y_log10()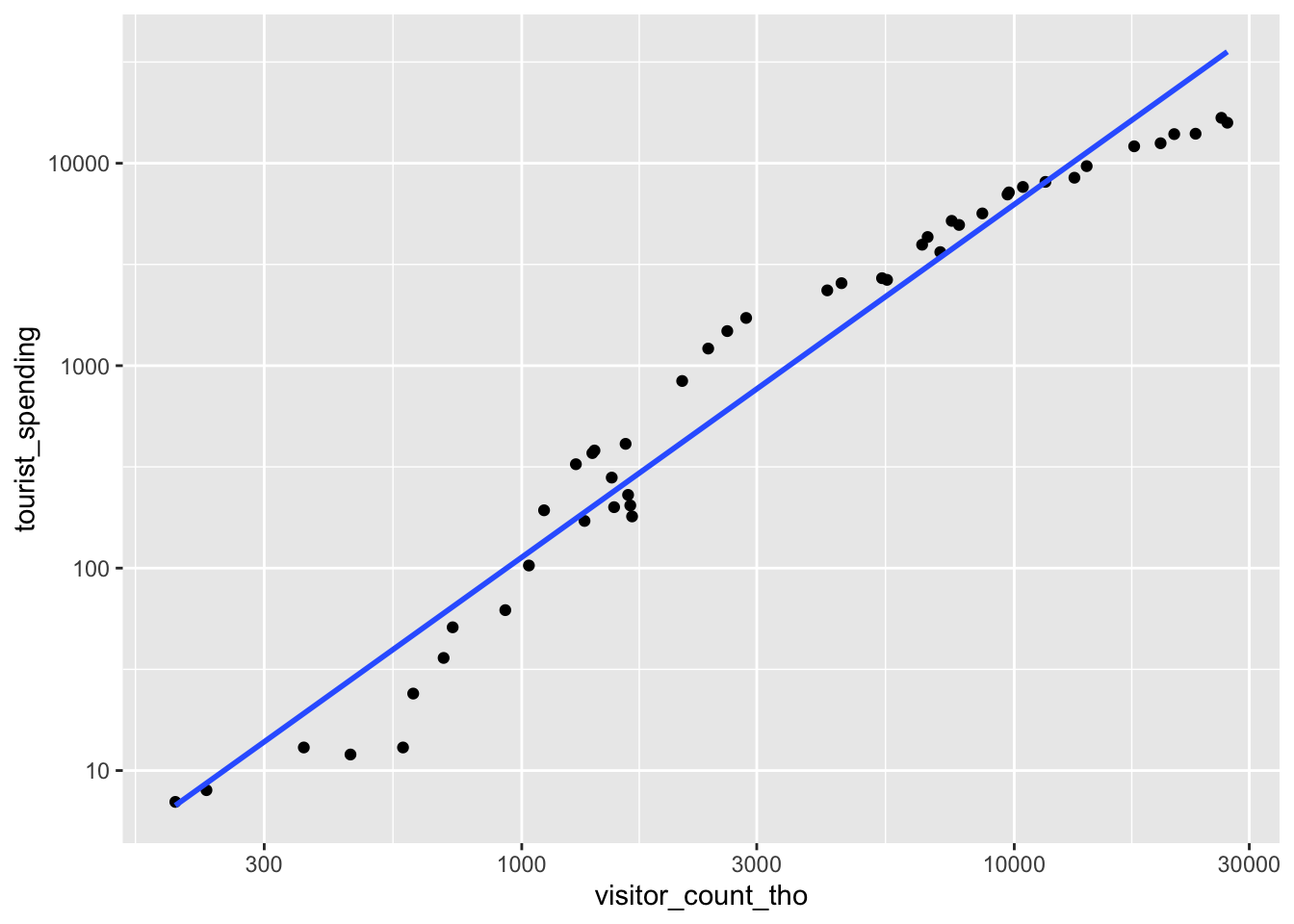
lm.out <- lm(visitor_count_tho ~ tourist_spending, data = tourism)
summary(lm.out)##
## Call:
## lm(formula = visitor_count_tho ~ tourist_spending, data = tourism)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -1672.01 -377.84 3.28 410.00 2674.76
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 636.75289 151.86868 4.193 0.000127 ***
## tourist_spending 1.49912 0.02466 60.786 < 2e-16 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 815.9 on 45 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.988, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9877
## F-statistic: 3695 on 1 and 45 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16lm.out.log <- lm(log(visitor_count_tho) ~ log(tourist_spending), data = tourism)
summary(lm.out.log)##
## Call:
## lm(formula = log(visitor_count_tho) ~ log(tourist_spending),
## data = tourism)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.49935 -0.14620 -0.01635 0.18520 0.58194
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 4.36409 0.12413 35.16 <2e-16 ***
## log(tourist_spending) 0.54839 0.01755 31.25 <2e-16 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.2813 on 45 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.956, Adjusted R-squared: 0.955
## F-statistic: 976.9 on 1 and 45 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16tourism$residual <- resid(lm.out)
tourism$residual.log <- resid(lm.out.log)
ggplot(tourism, aes(x = tourist_spending, y = residual)) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0) +
geom_point()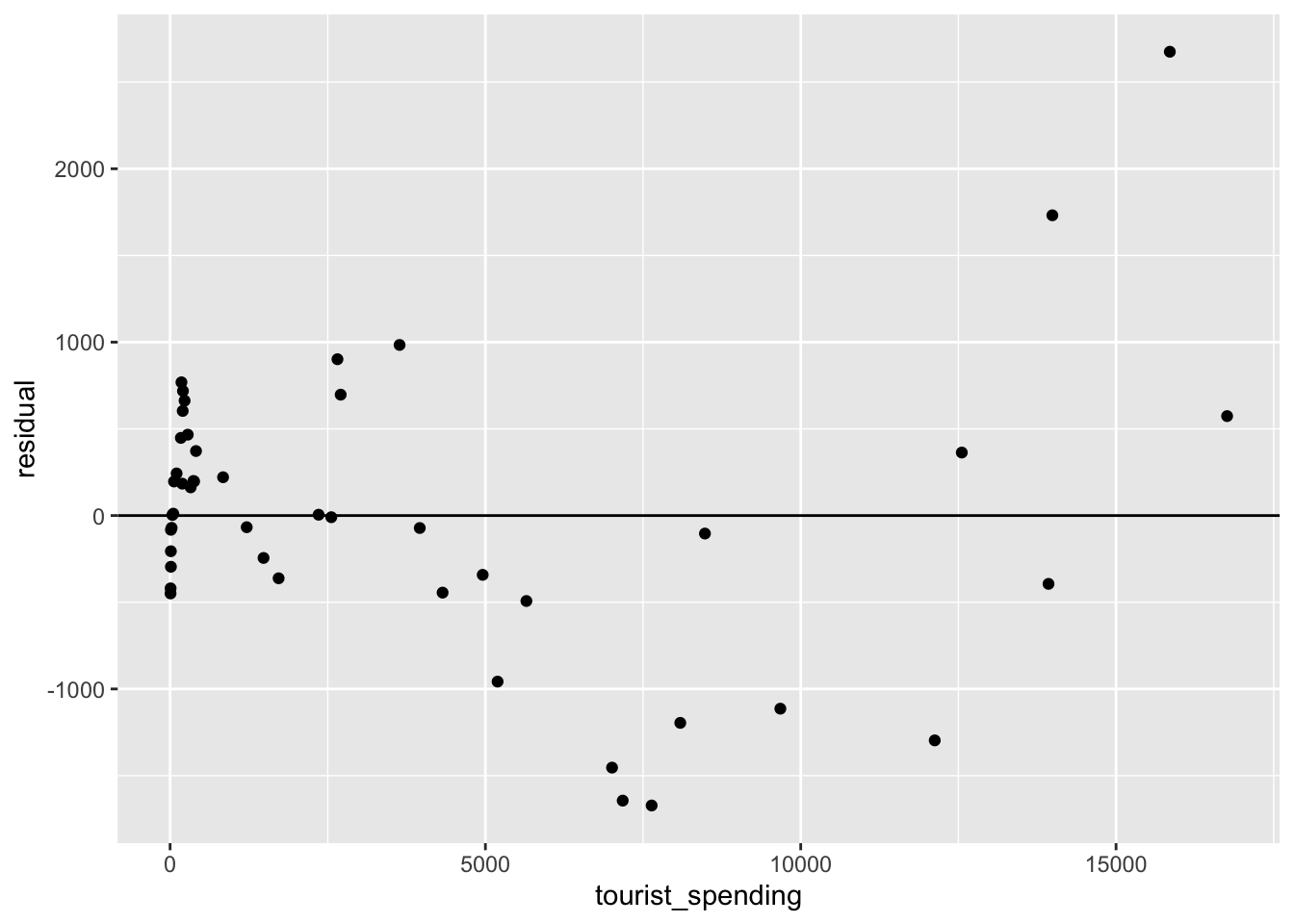
ggplot(tourism, aes(x = tourist_spending, y = residual.log)) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0) +
geom_point()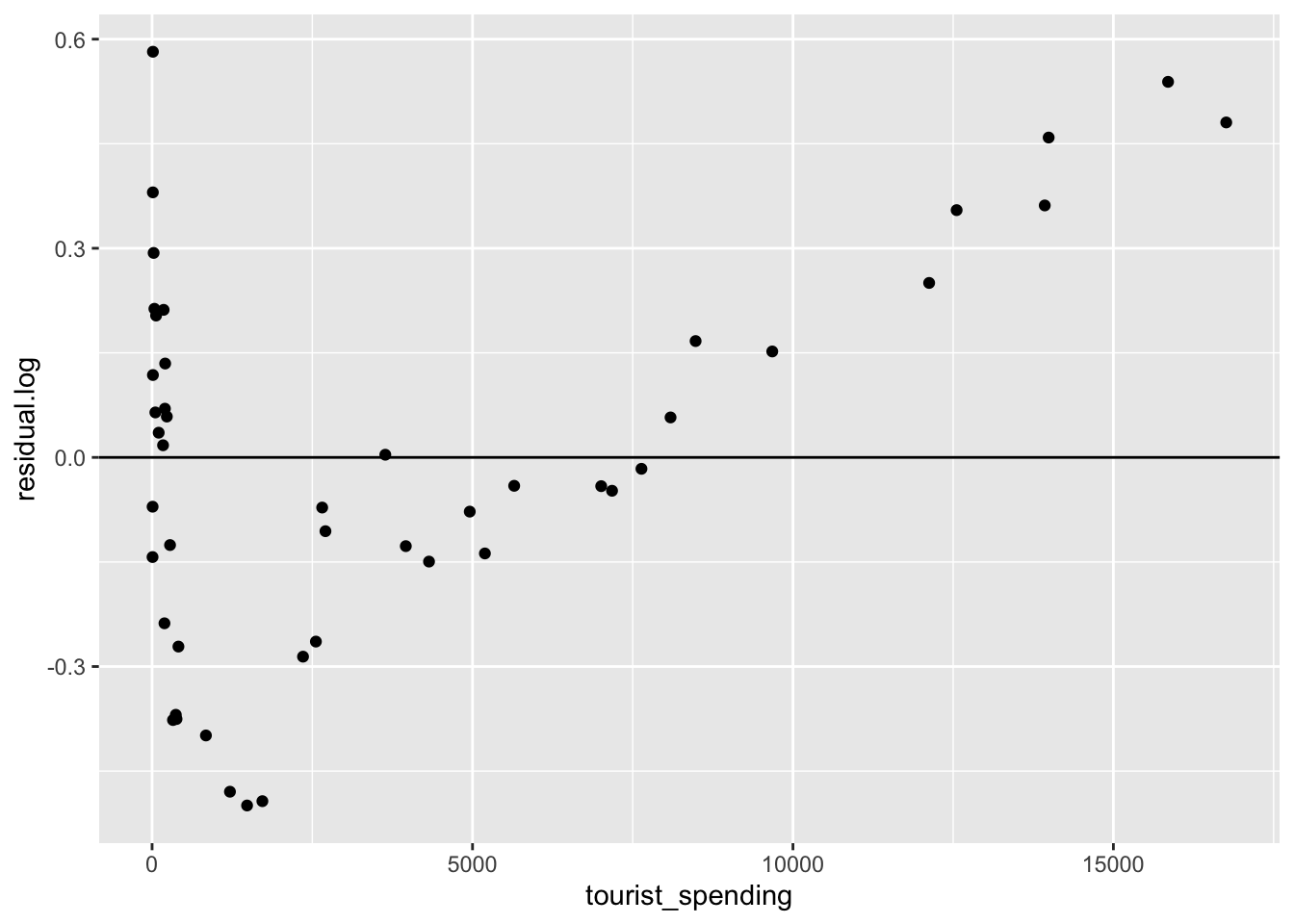
hist(tourism$residual)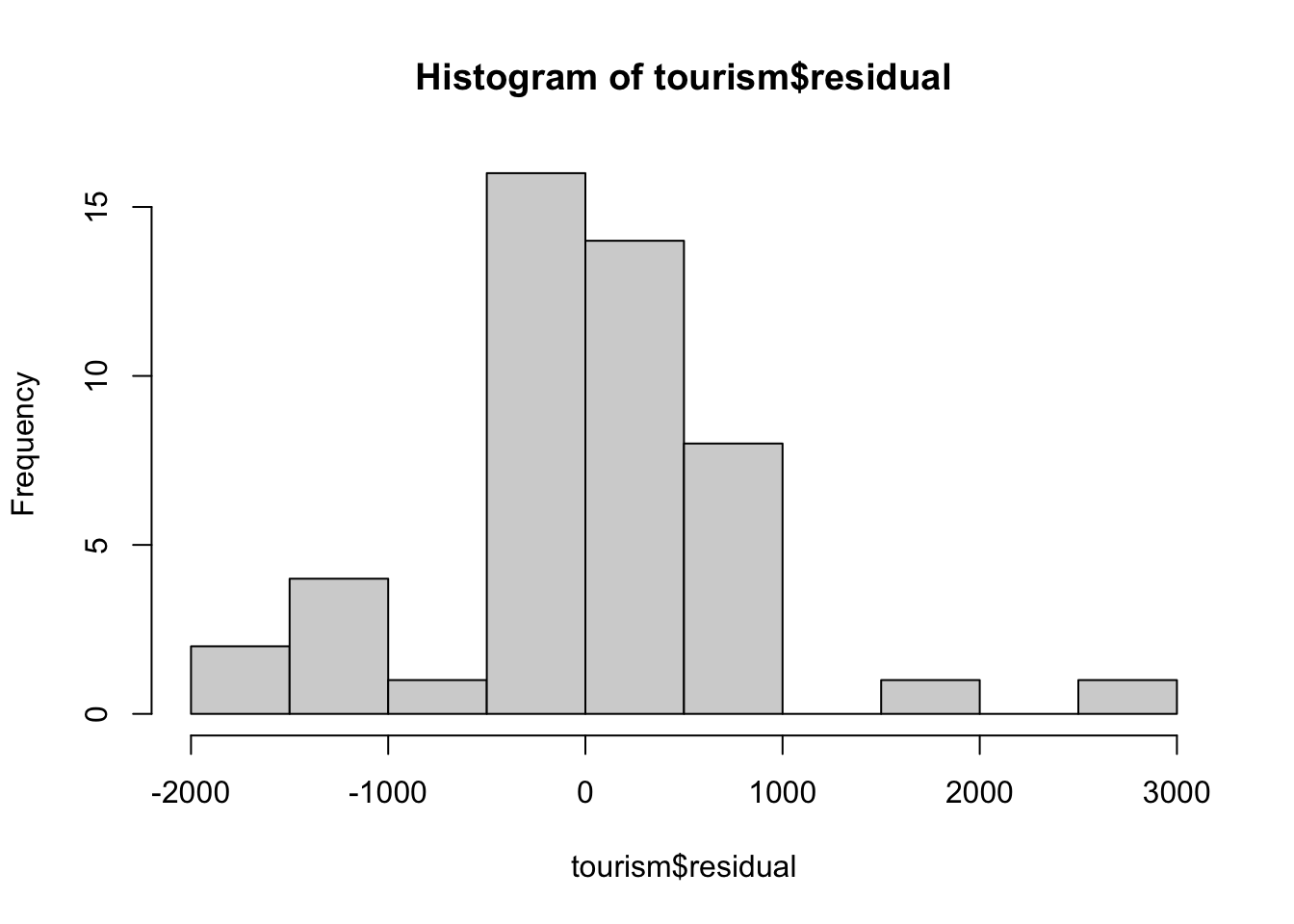
ggplot(tourism, aes(x = residual)) + geom_histogram(bins = 7)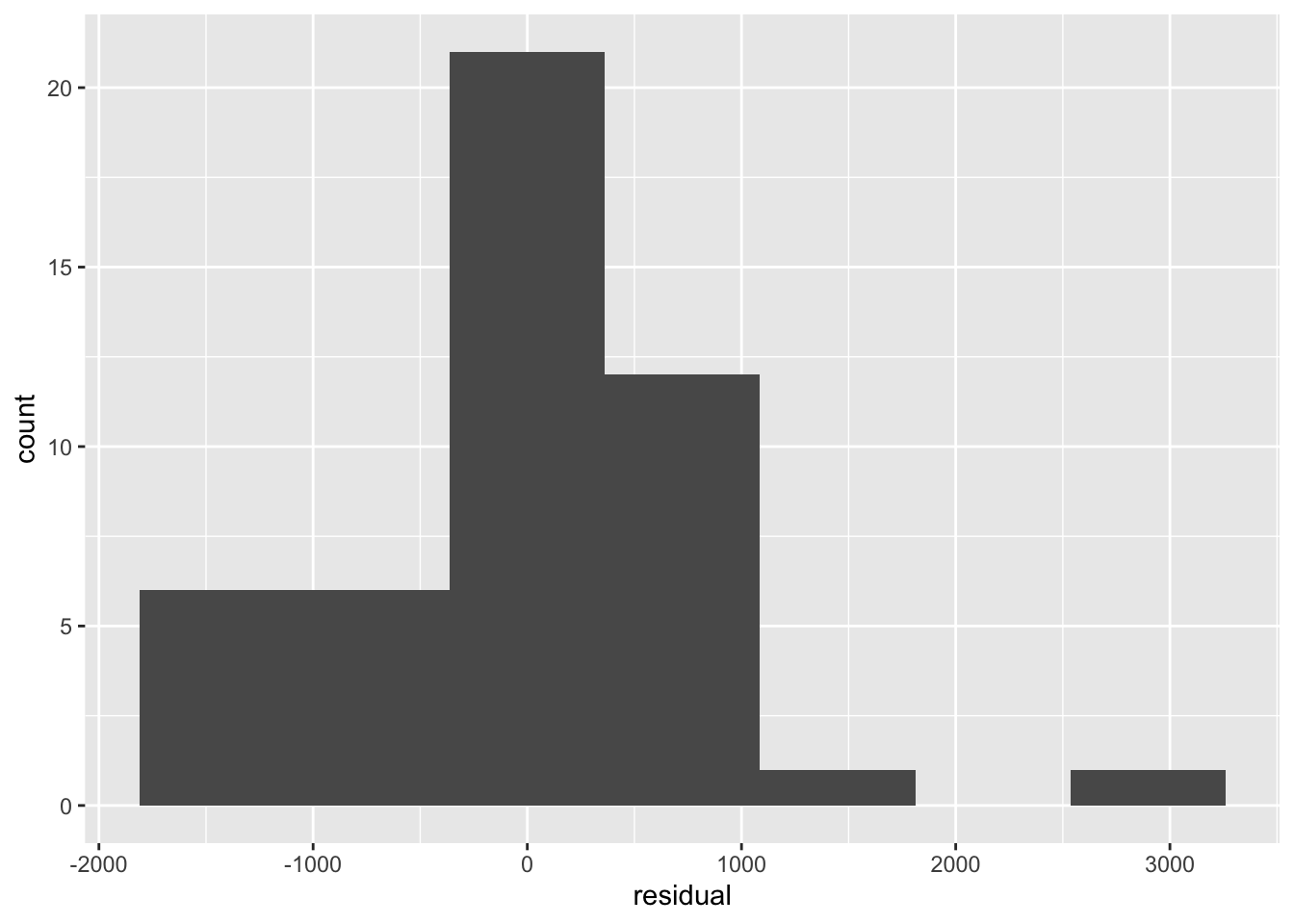
ggplot(tourism, aes(x = residual)) + geom_density()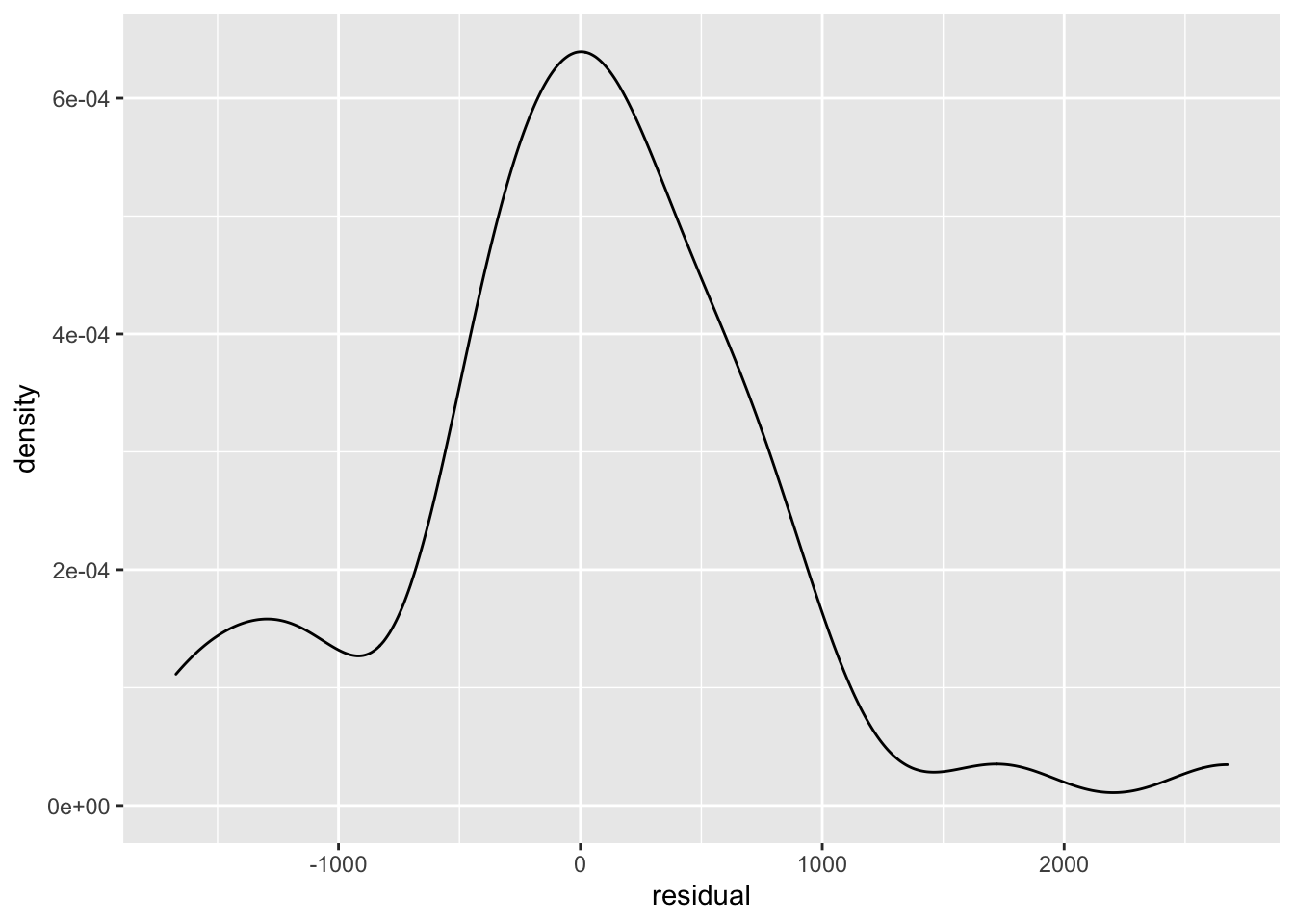
Here is the R script that looks at how the F-statistic is calculated.
poverty <- read.table("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jbryer/DATA606Spring2021/master/course_data/poverty.txt", h = T, sep = "\t")
names(poverty) <- c("state", "metro_res", "white", "hs_grad", "poverty", "female_house")
poverty <- poverty[,c(1,5,2,3,4,6)]
head(poverty)## state poverty metro_res white hs_grad female_house
## 1 Alabama 14.6 55.4 71.3 79.9 14.2
## 2 Alaska 8.3 65.6 70.8 90.6 10.8
## 3 Arizona 13.3 88.2 87.7 83.8 11.1
## 4 Arkansas 18.0 52.5 81.0 80.9 12.1
## 5 California 12.8 94.4 77.5 81.1 12.6
## 6 Colorado 9.4 84.5 90.2 88.7 9.6# Sample size
n <- nrow(poverty)
# Total variance for the outcome variable
SSy <- sum((poverty$poverty - mean(poverty$poverty))^2)
# Start with one predictor
lm.out1 <- lm(poverty ~ female_house, data = poverty)
summary(lm.out1)##
## Call:
## lm(formula = poverty ~ female_house, data = poverty)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -5.7537 -1.8252 -0.0375 1.5565 6.3285
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 3.3094 1.8970 1.745 0.0873 .
## female_house 0.6911 0.1599 4.322 7.53e-05 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 2.664 on 49 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.276, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2613
## F-statistic: 18.68 on 1 and 49 DF, p-value: 7.534e-05anova(lm.out1)## Analysis of Variance Table
##
## Response: poverty
## Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
## female_house 1 132.57 132.568 18.683 7.534e-05 ***
## Residuals 49 347.68 7.095
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1# Note that F-statistic is the same summary(lm.out1).
# From the ANOVA output, it is the ratio of mean square model
# (i.e. female_house here) to mean square error/residual.
132.568 / 7.095## [1] 18.68471# However, this only works with one predictor.
SSresid <- sum(lm.out1$residuals^2)
SSmodel <- SSy - SSresid
k <- length(lm.out1$coefficients) - 1
((SSmodel) / k) / (SSresid / (n - (k + 1)))## [1] 18.68348lm.out2 <- lm(poverty ~ female_house + white, data = poverty)
summary(lm.out2)##
## Call:
## lm(formula = poverty ~ female_house + white, data = poverty)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -5.5245 -1.8526 -0.0381 1.3770 6.2689
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) -2.57894 5.78491 -0.446 0.657743
## female_house 0.88689 0.24191 3.666 0.000615 ***
## white 0.04418 0.04101 1.077 0.286755
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 2.659 on 48 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.2931, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2637
## F-statistic: 9.953 on 2 and 48 DF, p-value: 0.0002422anova(lm.out2)## Analysis of Variance Table
##
## Response: poverty
## Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F)
## female_house 1 132.57 132.568 18.7447 7.562e-05 ***
## white 1 8.21 8.207 1.1605 0.2868
## Residuals 48 339.47 7.072
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1# How is the F-Statistic calculated
# Ho: All coefficients are zero
# Ha: At least one coefficient is nonzero
n <- nrow(poverty)
SSresid <- sum(lm.out2$residuals^2)
SSy <- sum((poverty$poverty - mean(poverty$poverty))^2)
SSmodel <- SSy - SSresid
k <- length(lm.out2$coefficients) - 1
((SSmodel) / k) / (SSresid / (n - (k + 1)))## [1] 9.952561